Introduction
Prerequisites: Graph Theory
Advanced topics on graph theory.
Bipartite Graph
A bipartite graph is a graph which can be partitioned into two sets such that no nodes in a set connect to another node in the same set.
Special Paths
A path is a certain order of visiting objects.
Hamiltonian Path
A Hamiltonian Path is a path that visits every node exactly once.
Eulerian Path
A Eulerian Path is a path that visited every edge exactly once.
Special Cycles
A cycle is a path that ends up at the same starting position.
Hamiltonian Cycle
A Hamiltonian cycle is a cycle that visits every node exactly once at ends back at the start.
Eulerian Cycle
A Eulerian Cycle is a cycle that visited every edge exactly once at ends back at the start.
Travelling Salesman Problem
The Travelling salesman is the problem where a salesman wants to find a cycle that minimizes the total cost of weights used of edges.
Special Nodes
Some graphs may have nodes that have special properties.
Root
A node in a directed acyclic graph that has no ancestors is a root.
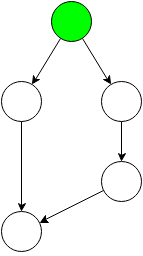
Center
The center of a undirected tree is the node that minimizes the sum of the distance to every other node. The center can be found be continuously stripping away leaf nodes (nodes with only one edge) layer by layer until either 1 or 2 nodes remain. The longest path in a tree will contain the center.