Introduction
Binary search is a type of search that is able to find an object in a sorted list in O(log n). In binary search, we first start at range and we keep trying to halve the problem until the range is narrowed down to a solution.
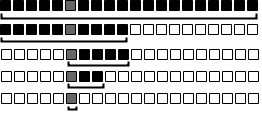
Example
For example, suppose we have a game where I told you I had a number from 1 to 100 and you would keep guessing a number. Every time you guessed, I would tell you if my number was higher or lower than your guess. We could use binary search to solve this problem in the most efficient way.
If my number was 17:
- You guess: 50
- I say lower.
So we know that: 1 <= number < 50. Since the number is less than 50, then we know we can eliminate all the numbers above 50. We just made the problem half as hard! The reason we picked 50 is important because it is the middle and it tells us the most information. If we picked 80 and the reply was higher it would narrow down the problem a lot, but if the reply was lower it would barely reduce the problem. Picking the middle works best because it tells us the most information if we get a "lower" or "higher" reply. So we should also guess the middle between 1 and 50.
- You guess: 25.
- I say lower.
So we know that 1 <= number < 25. Once again, we made the problem half as hard. Note that at every step we will make the problem half as hard. We need to pick the next middle number which is either 12 or 13, but we are indifferent because it will still tell us the most information (unless you get lucky).
- You guess 13.
- I say higher.
So we know that 13 < number < 25.
- You guess 19.
- I say lower.
So we know that 13 < number < 19.
- You guess 16.
- I say higher.
So we know that 16 < number < 19
- You guess 17.
- I say correct!
Generic Binary Search
This is a generic implementation of a binary search.
void binarySearch (int ans, int minVal, int maxVal) {
while(maxVal >= minVal) {
int mid = (minVal + maxVal) / 2;
if (mid == ans) {
return;
}
else if (mid < ans) {
minVal = mid + 1;
}
else if (mid > ans) {
maxVal = mid - 1;
}
}
}
Finding Number in Sorted Array
Suppose we have a sorted array and we want to find if a number X is in the array. We can do this easily by looping through the entire array and searching for the element we want. However, we can do better with binary search.
Let's say we start with the array [-6, -5, 1, 2, 5, 7, 10, 17, 23, 29] and we are looking for the element 2. We pick the middle element in the array which is 7 and we compare it with 5. Since 2 < 7, and everything in the last half the array is greater than 7, then everything in the last half the array is greater than 2 and there is no point searching there. Thus we have halved the work we need to do. We can do the same thing by picking the middle element of the first half [-6, -5, 1, 2, 5] which is 1. Since 2 > 1 and everything in the first half is less than 1, then everything in the first quarter is less than 1 and there is no point searching there. Thus the element 2 we are looking for should be in the 2nd quarter of the array [2, 5] which it is and we can return that it is found.
public static boolean exists(int[] arr, int x) {
int start = 0;
int end = arr.length - 1;
while (end >= start) {
int middle = (start + end) / 2;
if (arr[middle] == x) {
return true;
}
else if (arr[middle] < x) {
start = middle + 1;
}
else if (arr[middle] > x) {
end = middle - 1;
}
}
return false;
}
Exercises
- Given a sorted array, find the number of elements between the number A and number B inclusive. Example: 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 16, 20. Given A=5 and B=15, the number of elements between A and B is 3 (6, 8, 10).
- Given two sorted arrays, find the number of duplicate elements.
- Given two decimal numbers A and B, find A/B without using the division operation or using decimals.
- Write a square root function accurate to four decimal places that uses binary search.