Introduction
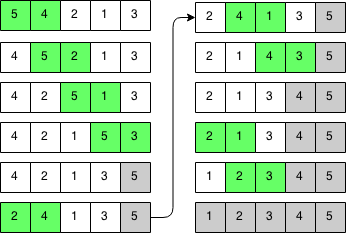
Bubble sort is one of the most basic sorting algorithms Its name describes how the algorithm works: bigger bubbles float to the top. Each time we pass through the array, we swap adjacent bigger elements with smaller elements. We keep passing through the array bubbling bigger elements to the top and until the array is sorted. It can be proved that you will need to pass through the array at most N times. Try to prove this for yourself.
Implementation
Bubble sort works by going through the array multiple times and swapping elements that are out of order as we go through the array. Every pass through the array, we move the largest element to the end.
Code
public static void bubbleSort(int array[]) {
// Keep going through array unless until no swaps are made.
boolean swapped = true;
while (swapped) {
swapped = false;
// Iterate through the array.
for (int j = 1; j < array.length; j++) {
// Swap if current element is bigger then next.
if (array[j - 1] > array[j]) {
// Swap two adjacent elements.
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j - 1];
array[j - 1] = temp;
swapped = true;
}
}
}
}