Introduction
A greedy algorithm is an algorithm that always selects the optimal next step towards the solution based on some property. Greedy problems are generally straightforward and easy to solve once you determine what property to maximize. However, the most difficult part is proving that greedy is the optimal solution for all cases.
Coin Problem
A cashier is given a $20 bill from their customer whose total comes to $14.67. How can the cashier give the change in the least amount of coins? Let's say our currency has denominations 1 cent, 5 cent, 10 cent, 25 cents, $1 and $2.
We can greedily use the biggest denomination as possible until we have no more coins. We need to make change for $5.33.
$5.33 - 2 • $2
= $1.33 - 1 • $1
= $0.33 - 1 • $0.25
= $0.08 - 1 • $0.05
= $0.03 - 3 • $0.01
= 0
The coin problem can only be solved greedily if the denominations fit nicely inside each other. Otherwise, the solution becomes more complicated. (See Dynamic Programming)
Implementation
int minCoins(int value) {
int denoms[] = { 1, 5, 10, 25, 100, 200 };
int totalCoins = 0;
// Iterate backwards by highest denomination.
for (int i = denoms.length; i >= 0; i--) {
// Calculate highest number of coins that can be used.
int coins = value / denoms[i];
// Increment number of coins.
totalCoins += coins;
// Subtract value of coins.
value -= denoms[i] * coins;
}
return totalCoins;
}
Interval Scheduling
Let's say you are at a festival and there are several special events that you want to attend, however the events may overlap at certain times. How can you pick the events that you go to such that you attend as many events as possible?
For example, we have the events below shown as a intervals on a timeline.
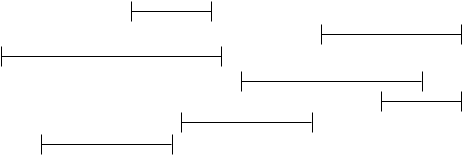
The first approach may seem to be greedily choosing the shortest intervals that do not overlap:

Another approach may be taking the earliest available event:
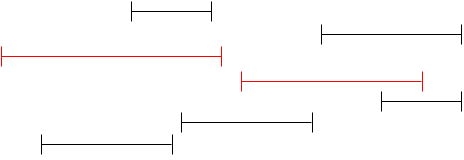
The above approaches seem to work, but they do not offer the optimal solution. We notice that we want to fit as many events as possible so we want to pick events that end as quickly as possible. So we can greedily select events with the earliest ending time.
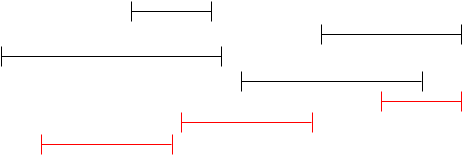
Note that although this approach does not give us the longest time spent at events, it gives us the most events that can be visited.
Implementation
class Interval implements Comparable<Interval> {
int start, end;
public Interval(int start, int end){
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
public int compareTo(Interval i) {
return end - i.end;
}
}
public int maxEvents(Vector<Interval> intervals) {
// Sort intervals by earliest end time.
Collections.sort(intervals);
int curTime = 0;
int events = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < intervals.size(); i++) {
// Find next interval greater or equal to current time.
while (i < intervals.size() && intervals.get(i).start < curTime) {
i++;
}
// Set current time as end of interval.
curTime = intervals.get(i).end;
// Increment number of intervals.
events++;
}
return events;
}
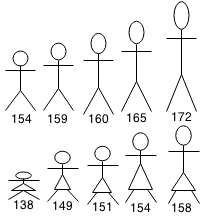
Couple Matching Problem
You are organizing a dance with a group of 10 men of varying heights and a group of 10 women of varying heights. The dance is done in pairs (a man and a women) and it is best performed when the pair is as close height as possible.
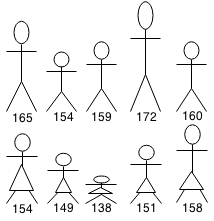
We can minimize the average height difference by sorting men and woman by height and then matching them.
Exercises
- Given N points and an interval size of S, find the minimum number of intervals required to cover all the points.
Given the future schedule of a stock, and starting with C dollars, what is the maximum amount of money you can make given that there is no commission?
For example you are given $1000, the future prices of a stock are: 100, 103, 105, 106, 101, 99, 95, 97.
- Buy 10 x $100 [$0]
- Sell 10 x $106 [$1060]
- Buy 11 x $95 [$15]
- Sell 11 x $97 [$1082]
You are on a road trip that is D km with N gas stations along the way and your gas tank has capacity C. Assuming that you start with a full tank, travel 1km/min, use 1L/km and the gas station fill rate is 5L/min, find the quickest time you can finish the trip in.
For example, if the total distance is 200km apart with tank capacity 80L and with 5 gas stations at 10km, 40km, 50km, 90km, 150km, the minimum time it will take is 224 minutes.