Introduction
A stack is an abstract data type with the property that it can remove and insert elements following a FILO (First In Last Out) structure. The first element to be inserted must be the last element to be removed and the last element to be inserted must be the first element to be removed. Sometimes, removal is called "pop" and insertion is called "push".
Imagine a stack of plates at a buffet, the plates are taken from the top and are also replaced from the top. The first plate to go in will be the last plate to come out. The last plate to go in will be the first to come out. This structure is what a stack is.
Example of push:
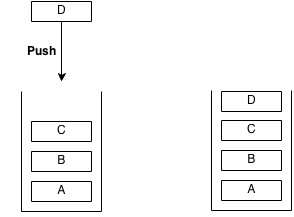
Example of pop:
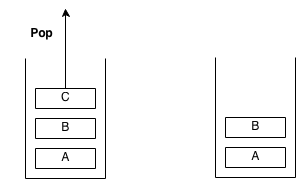
Stacks are used to keep track of function calls in memory. Whenever a function is called, it is placed on the memory stack with its variables, and when it is returning a value, it is popped off the stack.
A stack is usually implemented as a vector.
Implementations
| Implementation | Pop | Push |
|---|---|---|
| Vector | O(1) | O(1) |
Exercises
Given a string of brackets of either () or [], determine if the bracket syntax is legal (every opening bracket has a closing bracket from left to right).
Legal syntax:
- ( [ ( ) [ ] ] )
- ( ) ( ) [ ] ( ) ( )
Illegal syntax:
- ( ( ) ]
- ( ) [ ( ] )